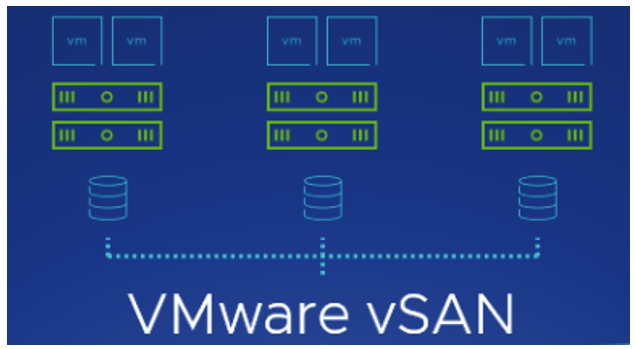
What is VMware vSAN?
VMware vSAN or Virtual Storage Area Network, is a software-defined storage (SDS) solution developed by VMware. Designed to seamlessly integrate with the vSphere platform, vSAN provides a layer of distributed storage, allowing organizations to leverage local server storage to create an efficient and flexible storage environment. In this article, we will explore in detail what vSAN is, its features, advantages, license types, requirements for implementation, use cases, recommendations, and conclusions.
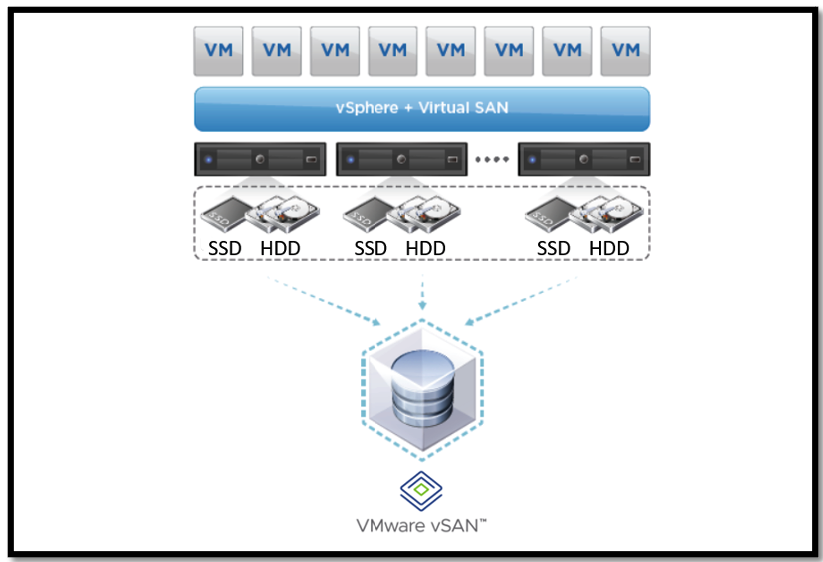
Features of VMware vSAN:
- Decentralized Storage: vSAN decentralizes storage, meaning that storage is not concentrated on a single device. This improves storage availability and scalability.
- Scalability: vSAN is scalable both horizontally and vertically. Horizontal scaling involves adding more ESXi servers to the vSAN cluster, while vertical scaling involves adding more storage capacity to each ESXi server.
- Automatic Storage Provisioning: vSAN automates the provisioning of storage for virtual machines, simplifying storage management and ensuring that virtual machines have the storage they need.
- Data Protection: vSAN offers various data protection features, including data replication, data compression, and data deduplication. These features help protect data against loss and corruption.
- Enhanced Resilience: Provides fault tolerance by replicating and distributing data among cluster nodes.
- Seamless Integration with vSphere: Integrates seamlessly with the vSphere platform, facilitating management and configuration through vCenter.
- Optimized Performance: Utilizes solid-state drives (SSD) for caching, significantly improving read and write performance.
- Custom Storage Policies: Allows the creation of storage policies at the virtual machine level to meet specific workload requirements.
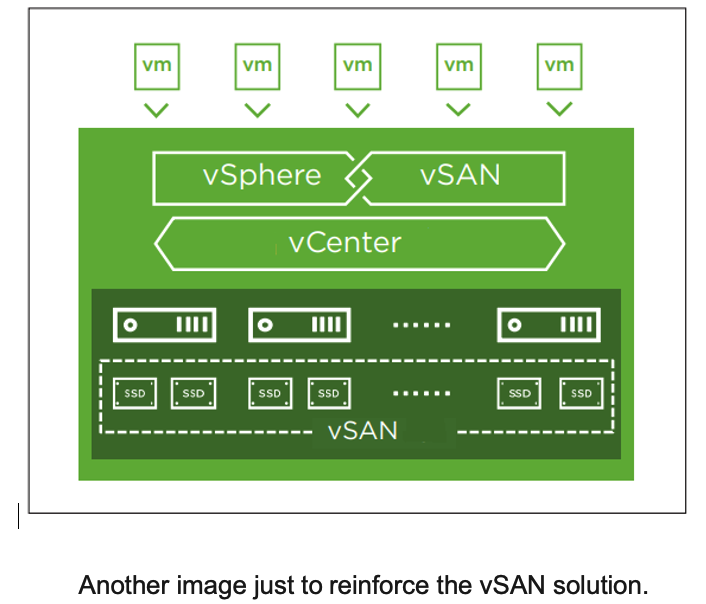
Advantages of VMware vSAN:
VMware vSAN offers a series of advantages for organizations using VMware vSphere. These advantages include:
- Cost Reduction: vSAN eliminates the need for dedicated external storage infrastructure, reducing hardware and management costs.
- Simplified Management: vSAN simplifies storage management by centralizing storage on a single platform.
- Improved Efficiency: vSAN can enhance storage efficiency by decentralizing storage and automating storage provisioning.
- Enhanced Fault Tolerance: Data replication and distribution among nodes ensure availability even in the event of hardware failures.
- Increased Performance: Leverages a combination of SSD and HDD disks to deliver optimal performance.
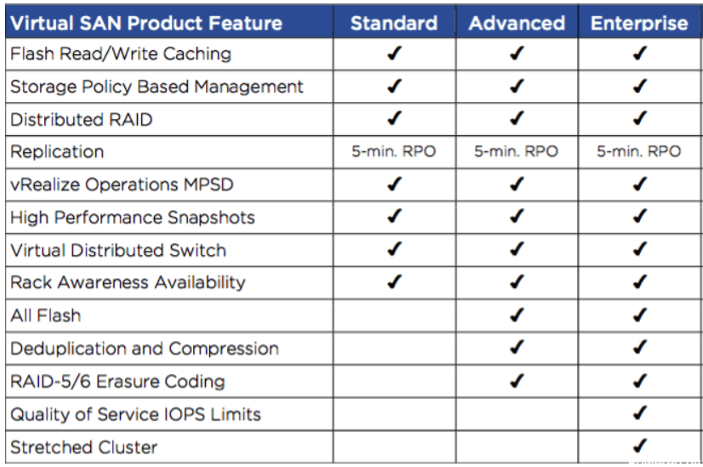
Types of VMware vSAN Licenses:
- VMware vSAN Standard: This license provides basic vSAN features such as decentralized storage, scalability, and automatic storage provisioning.
- VMware vSAN Enterprise: This license includes all the features of vSAN Standard, plus advanced features like data replication, data compression, and data deduplication.
- vSAN Enterprise: Includes enterprise features such as Quality of Service (QoS) and the ability to add write cache on SSD.
- VMware vSAN for vSphere with Tanzu: This is a special type of license that provides vSAN Enterprise features along with support for containers and Kubernetes.
Requirements for VMware vSAN:
- Minimum ESXi Servers: A minimum of three (03) ESXi servers is recommended for the initial vSAN implementation, but it can be scaled to more nodes as needed.
- Minimum Disks per Server: Each server must have at least one SSD for cache and one HDD for capacity, but additional disks can be added based on performance and capacity requirements.
- vSAN Storage Drive: The vSAN storage drive is used to store vSAN data and must have at least 100 GB of free space.
- vSAN Network: The vSAN network is a dedicated network used to connect ESXi servers and vSAN storage drives. A speed of at least 1 Gbps is recommended for the data network, and 10 Gbps or more for the vSAN network.
- Disk Types: SATA, SAS, or NVMe disks can be used depending on performance and capacity needs.
Other Important Points:
In addition to the features, advantages, and license types mentioned earlier, there are other important points to consider when evaluating VMware vSAN. These points include:
- Compatibility: VMware vSAN is compatible with a wide range of server and storage hardware.
- Management: VMware vSAN can be managed through the vSphere user interface or via the command line.
- Support: VMware provides technical support for VMware vSAN.
Use Cases:
- Infrastructure Virtualization: To consolidate and virtualize servers, efficiently utilizing local storage.
- VDI Environments: Provides efficient and high-performance storage for virtual desktop environments.
- Private Cloud Deployments: Easily scales to support the needs of a private cloud, providing agile storage.
Steps to Implement VMware vSAN:
1.- Planning: Determine storage requirements, the number of required ESXi hosts, and the vSAN license type.
2.- Hardware Preparation: Install ESXi hosts, configure the network, and prepare local storage.
3.- vSAN Configuration: Configure vSAN using the vSphere Client interface or command line.
4.- Virtual Machine Provisioning: Once vSAN is configured, virtual machines can be provisioned.
Conclusion:
VMware vSAN is a powerful and flexible storage solution that can offer numerous benefits for organizations using VMware vSphere. If you are seeking a hyper-converged storage solution for your vSphere environment, VMware vSAN is a choice worth considering.





