La Tecnología hecha fácil en Español y ahora en English
For the implementation of Zabbix as a monitoring service for VMware, I am using a virtual machine with the following details:
Operating System: Ubuntu.
I will start assuming that you know how to install Ubuntu. If you are unfamiliar, don’t worry; a default installation where you only need to press the «next» button is sufficient for this lab.
Install the tasksel package, which we will later use to install Apache, MySQL, and PHP. In Ubuntu, you can use a single command to install all three services along with their packages..
Now, using tasksel, we install all the necessary packages with a single command:
The installation process begins; you just need to wait for it to finish.
Execute the following commands:
# wget https://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/6.0/ubuntu/pool/main/z/zabbix-release/zabbix-release_6.0-1+ubuntu22.04_all.deb
# wget https://repo.zabbix.com/zabbix/6.0/ubuntu/pool/main/z/zabbix-release/zabbix-release_6.0-1+ubuntu20.04_all.deb
As I already had the package downloaded from the above address, I copied it to Linux and installed it from that directory using the same dpkg command:
# dpkg -i zabbix-release_6.0-1+ubuntu22.04_all.deb
Updating the repositories to incorporate the changes:
# apt update
The update process begins.
# apt list –upgradable
To display all the packages that can be upgraded, use:
Now, execute the command for the update, adding the -y attribute to install without asking for confirmation:
# apt upgrade -y
The installation process begins…
At this point, we have the system with everything necessary to proceed with the installation of Zabbix.
We need to install several components, but we can install them all with a single command and installation process:
# apt install zabbix-server-mysql zabbix-frontend-php zabbix-apache-conf zabbix-sql-scripts zabbix-agent
CONTINUE…..
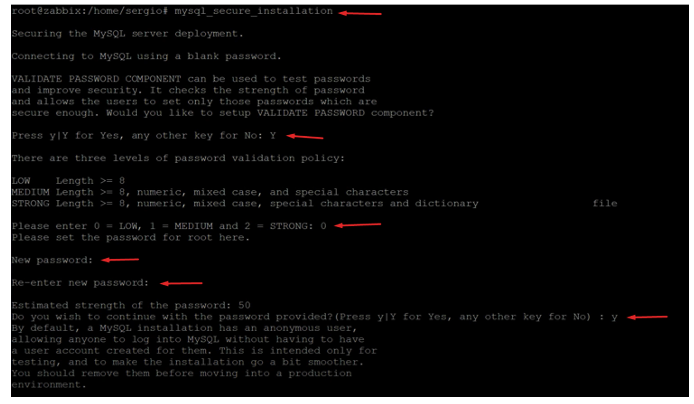
# mysql_secure_installation
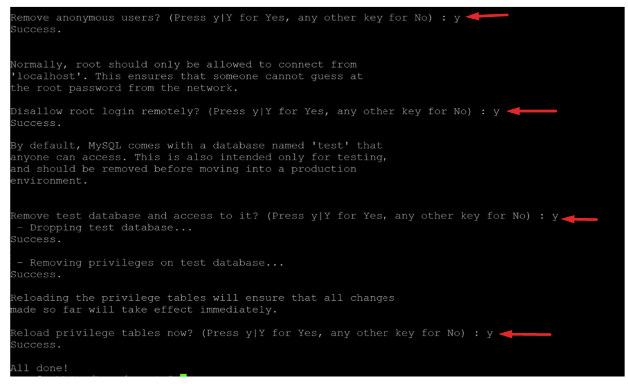
And it will ask us a series of questions:
It doesn’t ask if we want a strong password = y
Let’s select the password strength level = 0
Enter the password = Santi.2023
Confirm if we agree with the provided password = y
CONTINUE….
It asks us:
Remove anonymous user = y
Disable remote login with the root account = y
Remove the Test database = y
Reload the privilege tables = y
DONE
Here is another way to change the password:
# mysql
mysql> ALTER USER ‘root’@’localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘S4nt14g0.2023’;
mysql> quit;
Log in to MySQL with the root user and the password we added in the previous step:
# mysql -u root -p
password
Create the database named ‘zabbix’ with the collate ‘utf8mb4_bin’:
mysql> create database zabbix character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin;
Create the user and password that we will use to connect Zabbix with MySQL:
mysql> create user zabbix@localhost identified by ‘Zabbix.2023’;
Grant permissions to the newly created user on the newly created database:
mysql> grant all privileges on zabbix.* to zabbix@localhost;
mysql> quit;
# mysql
# set global log_bin_trust_function_creators = 1;
# quit;
# zcat /usr/share/zabbix-sql-scripts/mysql/server.sql.gz | mysql -u zabbix -p zabbix
Enter password: Zabbix.2023
# vi /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf
Search for DBUser=Zabbix, uncomment #DBPassword, and set the password you are using.
The configuration should look like this:
—————————————————-
DBUser=zabbix
### Option: DBPassword
# Database password.
# Comment this line if no password is used.
#
# Mandatory: no
# Default:
DBPassword=Zabbix.2023
——————————————————
EDIT
# vi /etc/zabbix/apache.conf
Search for the following line:
# php_value date.timezone Europe/Riga
Uncomment the line and set the time zone:
# php_value date.timezone America/Santiago
If you need different time zones, here is the link:
The language configuration is only to ensure there are no issues with the interface output.
# locale-gen «en_US»
# systemctl restart zabbix-server zabbix-agent apache2
# systemctl enable zabbix-server zabbix-agent apache2
To do this, simply open your preferred web browser and enter the following URL:
http://host-IP/zabbix
Replace host-IP with the IP address of the Zabbix server you just installed:
A window will appear with the pre-check and the status of each one; they should all be OK.
The next window will ask for the database connection details. These are the details we configured earlier. Press the NEXT button to continue.
Validate the time zone and the name of the Zabbix server, then press NEXT.
A summary of the entire pre-installation will be displayed. Review it and press NEXT to continue, then FINISH to complete.
From there, you just need to log in again and proceed with the configuration of vCenter or the ESXi host.
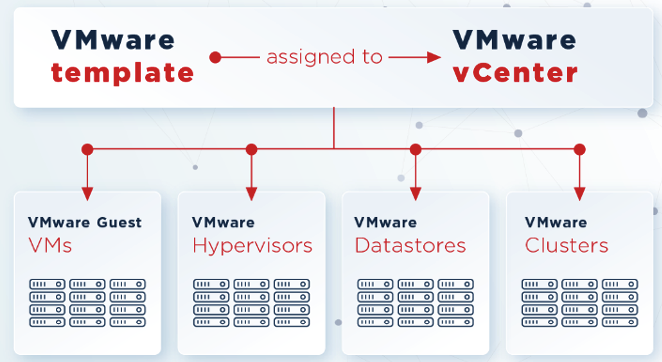
Now, within the Zabbix Web Administration console, we can configure vCenter or ESXi hosts. When adding vCenter, this process will automatically discover the hosts that are part of vCenter. So, the process of adding ESXi hosts is in case you don’t have vCenter.
1.- Go to Configuration > Hosts > Create host.
2.- Enter the Host name (e.g., vcenter).
3.- Enter Visible Name (e.g., VMware vSphere).
4.- Select Groups (any, e.g., Hypervisors).
5.- In Interfaces, enter the IP address of the vCenter with port 10050 (optional).
6.- Go to Macros.
7.- Create 3 Macros like these:
{$URL} with the value of your vCenter URL.
{$USERNAME} with the value of your vCenter username.
{$PASSWORD} with the value of your vCenter password.
8.- Enter a Password, URL, and Username of the vCenter in the Values fields. Go to Templates and
9.- link the template «Template VM VMware.»
10.- After All Configurations, click on Add.
11.- This will take some time from the vCenter the first time, as much as 1 or 2 hours or more.
12.- As soon as it fetches the data from vCenter, you will be able to see all the discovered items from vCenter, such as Datacenters, Clusters, ESXi Hosts, and Virtual Machines.
13.- To view all the information, go to Configurations > Host groups.
And that’s it! You have now added vCenter.
To add a standalone ESXi host, we need to perform several activities:
Let’s get started:
# vi /etc/zabbix/zabbix_server.conf
And then in the line LogFile=/var/log/zabbix/zabbix_server.log
LOOK FOR THE FOLLOWING VALUES AND UNCOMMENT THEM:
StartVMwareCollectors
VMwareFrecuency
VMwarePerfFrecuency
VMwareCacheSize
VMwareTimeout
# sudo systemctl restart zabbix-server
Navigate to Host -> Manage -> System -> Advanced Settings -> Filter by enablemob.
4.- Edit the value to True.
Find the UUID of the ESXi Host:
https://IP-Host-ESXi/mob/?moid=ha-host&doPath=hardware.systemInfo
curl –insecure -s -u your_esxi_username:your_esxi_password
https://your_esxi_host/mob/?moid=ha-host&doPath=config.uuid
5.- Create the Zabbix user on the ESXi host:
6. Grant permissions to the new user on the ESXi host:
10. The user is now added:
11. Now, let’s go to Zabbix:
Navigate to Configuration -> Hosts in the Zabbix web interface.
12. Click on «Create Host»:
13. In the «New Host» window, in the «Host» tab, add the following details:
Host Name
Template = VMware hypervisor ICM Ping
Groups = Template/Virtualization
Agent = add the Host’s IP or hostname
THEN go to the «Macros» tab:
Create the following macros:
{$VMWARE.PASSWORD} = Kapsch.2023
{$VMWARE.URL} = https://192.168.233.13/sdk
{$VMWARE.USERNAME}=zabbix
{$VMWARE_PERF_INTERVAL} = 5m
{$VMWARE.HV.UUID} = = Valor del UUID del Host
CLIC boton ADD
Finally go to Menu Monitoring Lastest data and filter by host added APPLY
We will now start seeing the collected data: